
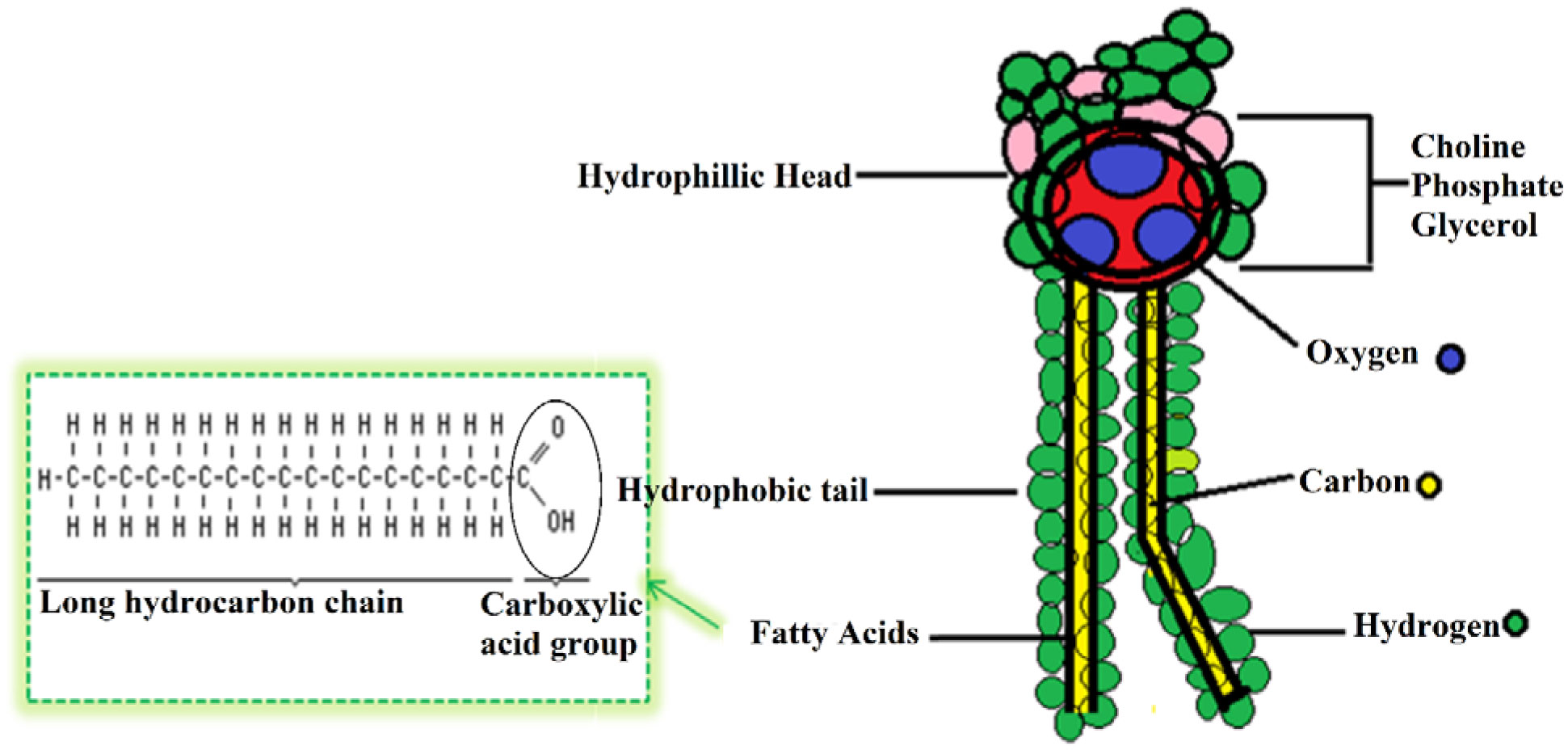
Phospholipid bilayers are the main structural component of the cell membranes. That is the dominant structural motif of the membranes of all cells and of some other biological structures, such as vesicles or virus coatings. The result is often a phospholipid bilayer: a membrane that consists of two layers of oppositely oriented phospholipid molecules, with their heads exposed to the liquid on both sides, and with the tails directed into the membrane. In aqueous solutions, phospholipids are driven by hydrophobic interactions, which result in the fatty acid tails aggregating to minimize interactions with the water molecules. The hydrophilic end usually contains a negatively charged phosphate group, and the hydrophobic end usually consists of two "tails" that are long fatty acid residues. Phospholipids in biological membranes Arrangement The first phospholipid identified in 1847 as such in biological tissues was lecithin, or phosphatidylcholine, in the egg yolk of chickens by the French chemist and pharmacist Theodore Nicolas Gobley. Purified phospholipids are produced commercially and have found applications in nanotechnology and materials science. The combination provides fluidity in two dimensions combined with mechanical strength against rupture. In eukaryotes, cell membranes also contain another class of lipid, sterol, interspersed among the phospholipids. They can form lipid bilayers because of their amphiphilic characteristic. Phospholipids are a key component of all cell membranes. The phosphate group can be modified with simple organic molecules such as choline, ethanolamine or serine. Marine phospholipids typically have omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA integrated as part of the phospholipid molecule. Phospholipids are a class of lipids whose molecule has a hydrophilic "head" containing a phosphate group and two hydrophobic "tails" derived from fatty acids, joined by an alcohol residue (usually a glycerol molecule). It is also a source for choline in the synthesis of acetylcholine in cholinergic neurons. Phosphatidylcholine is the major component of lecithin.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
